Backup and Restore DATAMIMIC Data¶
Warning
The current page still doesn't have a translation for this language.
But you can help translating it: Contributing.
This guide explains how to backup and restore data in your DATAMIMIC instance, helping you safeguard your configuration and generated data.
Danger
The backup and restore process is critical—handle with extreme care. Any misstep could lead to irreversible data loss, so please verify each step.
Note
Before backup or restore operation, the administrator should create a banner to notify all users about the maintenance due to the instance will be locked down during the operation.
Overview¶
DATAMIMIC provides a comprehensive backup and restore system that captures the critical data components of your instance:
- PostgreSQL database (tables, relationships, configurations)
- MinIO storage (templates, user data, snapshots)
- Redis data (caching and temporary storage, logging data)
Creating a Backup¶
Prerequisites¶
- You must have administrator privileges to access the backup functionality
- Ensure you have enough disk space for the backup file
Steps to Create a Backup¶
- Navigate to User Dashboard → System Maintenance → Create Backup
- Click on the Create Backup button
- Confirm the backup creation when prompted
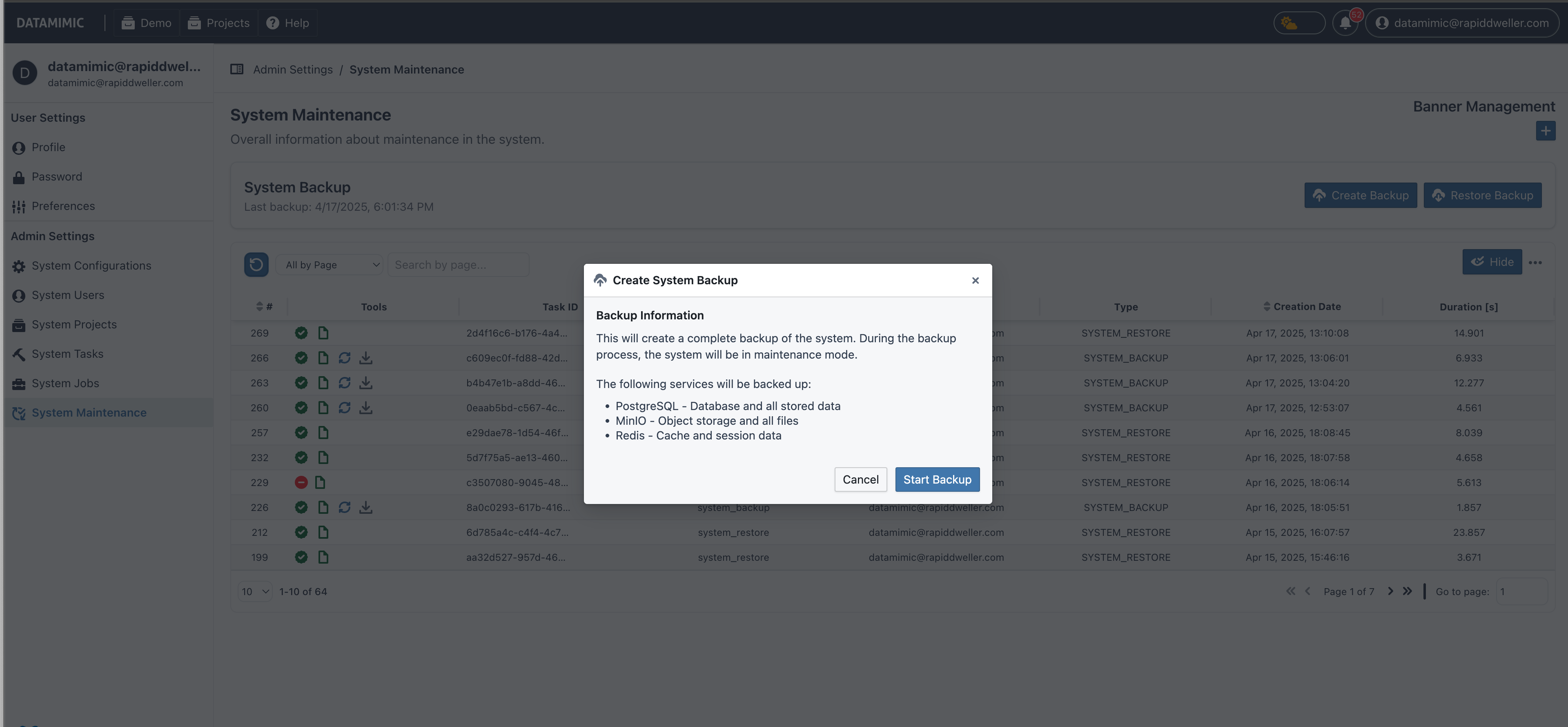
What Happens During Backup¶
When a backup operation is initiated:
- DATAMIMIC automatically enters Maintenance Mode
- Only administrator users can log in during this period
- Other users are redirected to a maintenance page with a message
- The system takes snapshots of:
- PostgreSQL database (excluding system-related tasks)
- MinIO buckets (excluding artifact buckets)
- Redis data
- The backup data is compressed into a single ZIP file
- Once complete, the system exits Maintenance Mode
Accessing Backup Files¶
Completed backups are stored as task artifacts. To download a backup:
- Navigate to the task list and find your backup task
- Download the artifact from the task details page
For more information on accessing task artifacts, see the Task Artifacts documentation.
Details of Backup Files¶
The DATAMIMIC backup process creates a ZIP file that bundles all relevant data. When extracted, you'll find a toml file containing metadata about the backup. This metadata primarily provides administrators with key information such as the timestamp, backup ID, and the DATAMIMIC version (both platform and core) at the time of the backup, as well as details about the underlying databases (e.g., PostgreSQL version, Redis version, etc.).
Since the archive also contains the actual backup data, it is recommended that you store this file securely.
Restoring from a Backup¶
Danger
Restoring from a backup will overwrite your current DATAMIMIC data. This operation cannot be undone. Make sure to create a backup of your current data before proceeding if needed.
Restore Methods¶
DATAMIMIC offers three methods to restore your instance:
Method 1: Restore from an Existing Backup Task¶
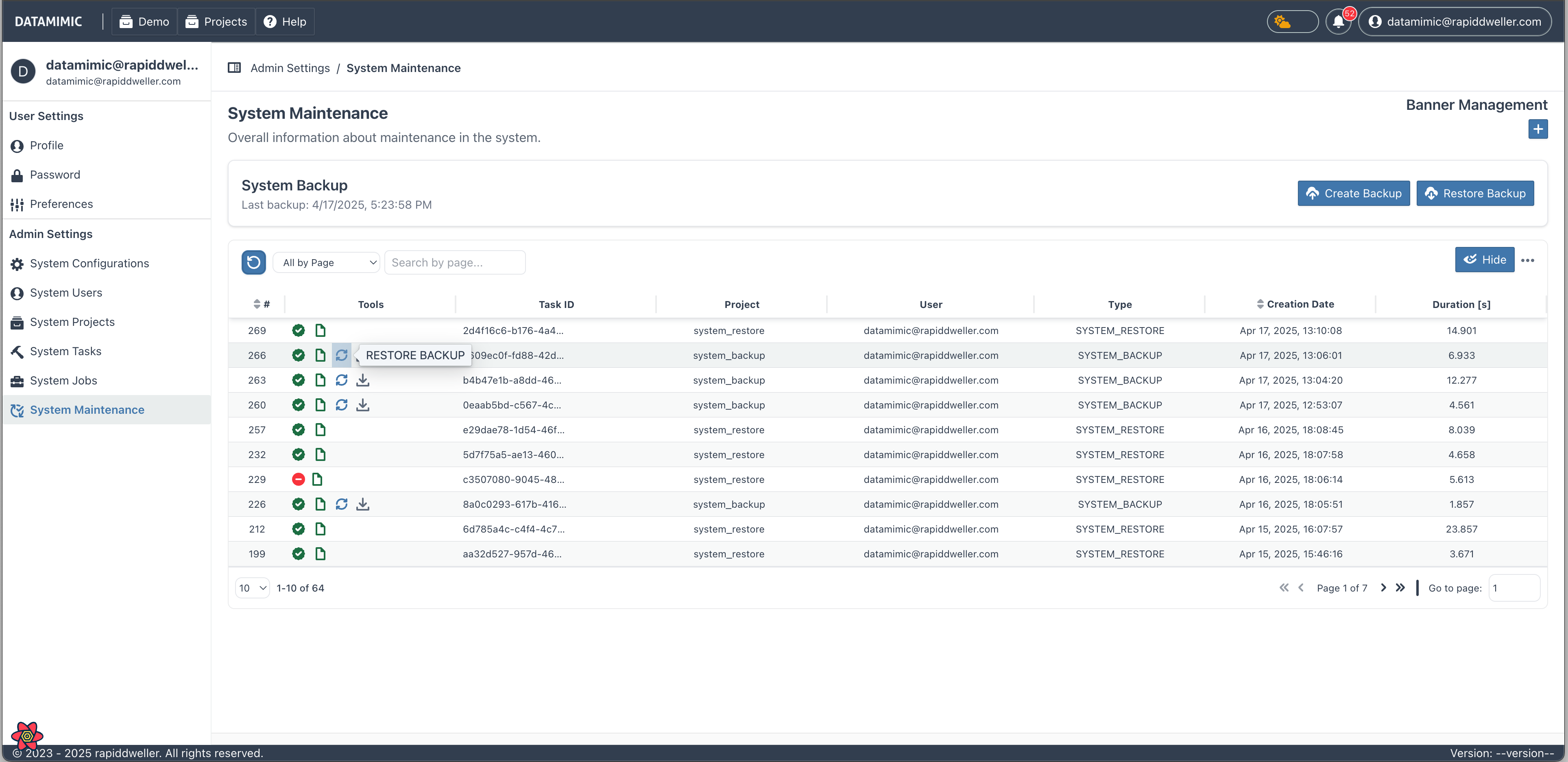
If the backup was created in your current instance:
- Navigate to User Dashboard → System Maintenance
- Select the backup task from the list of available backups
- Click on Restore from Selected Backup
- Confirm the restoration when prompted
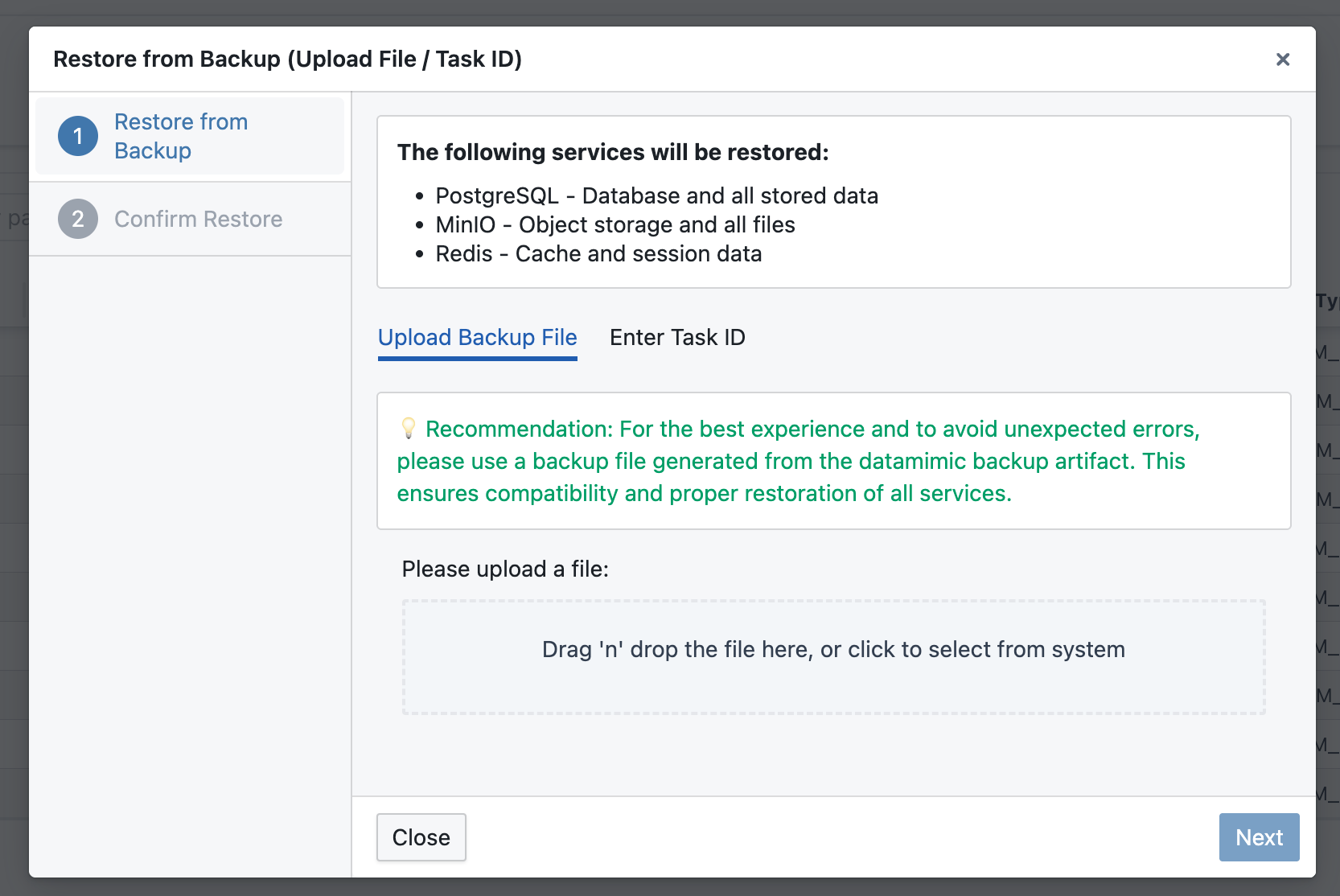
Method 2: Upload a Backup File¶
If you have a backup file from another instance or previously downloaded:
- Navigate to User Dashboard → System Maintenance
- Click on Restore Backup, select Upload Backup file
- Select your backup file (.zip format created by DATAMIMIC Backup)
- Click on Restore from Uploaded Backup
- Confirm the restoration when prompted
Method 3: Restore from a Backup ID Uploaded Directly to MinIO¶
If you have access to DATAMIMIC's instance MinIO, you can upload the backup file directly into MinIO either through MinIO UI or CLI. Then you can perform the Restore process from DATAMIMIC's UI.
- Upload the backup zip file directly to MinIO:
- Use MinIO UI or MinIO CLI tool to upload the zip backup file directly to MinIO.
- The backup needs to be inside the "backup" bucket and inside a top-level directory object
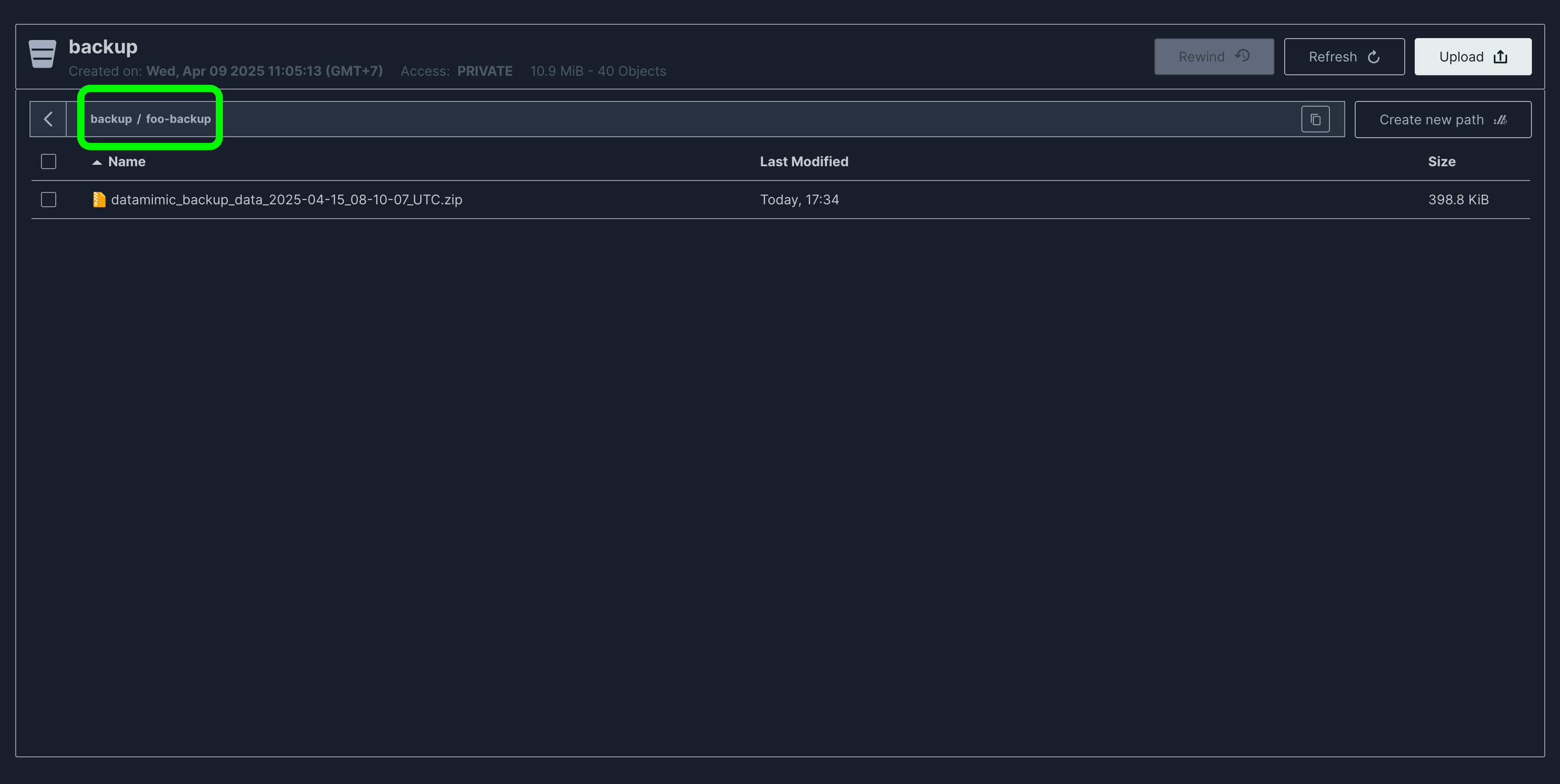
-
As you can see from the example image, our backup file is inside a
foo-backupdirectory which is inside the "backup" bucket. Thisfoo-backupwill be used as thebackup-idwhen performing the restore process in DATAMIMIC's UI -
Navigate to User Dashboard → System Maintenance → Restore Backup
- Select Enter Backup ID
- Enter the backup ID of the backup file that was uploaded in step 1 to MinIO (in this example,
foo-backup) - Confirm the restoration when prompted
What Happens During Restore¶
When a restore operation is initiated:
- DATAMIMIC automatically enters Maintenance Mode
- Only administrator users can log in during this period
- Other users are redirected to a maintenance page with a message
- Current data is cleared from:
- PostgreSQL database
- MinIO specified buckets
- Redis storage
- Data from the backup is restored to each system
- Once complete, the system exits Maintenance Mode
Best Practices¶
- Create regular backups of your DATAMIMIC instance, especially before major configuration changes
- Store backup files in a secure, external location
- Test restoration procedures in a non-production environment before using in production
- Document the contents and date of each backup file
- Monitor the available disk space for backup operations
Troubleshooting¶
If you encounter issues during backup or restore:
- Check the task logs for detailed error information
- Because the system is under maintenance, regular users will not have access to the application. However, an administrator can still log in and deactivate the maintenance mode manually
- Ensure your instance has sufficient disk space
- Verify that all services (PostgreSQL, MinIO, Redis) are running properly
- Contact DATAMIMIC support if issues persist
Limitations¶
- System-related tasks are excluded from backups to prevent conflicts during restoration
- If the restore target is a fresh instance (without any data), the new task data will only include tasks related to projects
- If the restore target is on the same instance (with existing data), the new task data will combine with existing system task data
- Artifact and demo data in MinIO are not included in backups to reduce file size
- Very large databases may require additional time for backup and restore operations